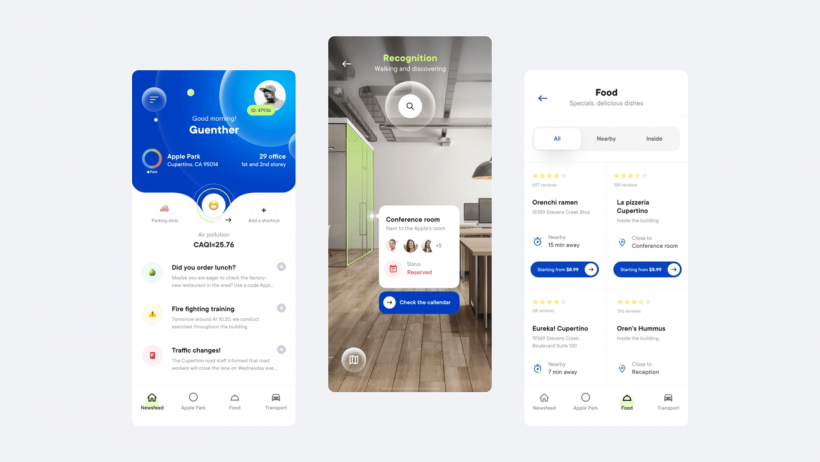
Augmented reality (AR) is expected to expand the utility industry's horizons, increase operational effectiveness, enhance customer service, cut down on repair times, slash training costs, and reduce accident risks.
A separate device is normally needed for virtual reality, which immerses people in a wholly artificial world, while augmented reality blends the best aspects of both. This is accomplished by incorporating audio-visual components using mobile devices and purpose-built AR software apps.
Tasks at utility companies are complex, which puts stress on engineering staff. This work can typically take a full workweek to accomplish. This article will discuss how augmented reality (AR) for businesses can enable great improvements.
“I am excited about Augmented Reality because unlike Virtual Reality, which closes the world out, AR allows individuals to be present in the world but hopefully allows an improvement on what’s happening presently.” - Tim Cook, Apple CEO
What Are the Uses of AR in the Energy and Utilities Sector?
The use of AR glasses or smart devices enhances a real environment with computer sounds, videos, and graphics. When the user points the device at a real object, the technology overlays digital elements on top of them.
Consider utility mapping, a method for making a thorough map of the underground wires, pipelines, and other infrastructure at a specific location. Engineers can avoid breaking lines when excavating thanks to the detailed AR map.
Utility mapping with augmented reality can help:
1.Data collection. About-site surveys, satellites, GPS-based systems, and LiDAR-equipped drones are all used to collect data on utility lines.
2.Data uploading. After that, a geographic information system is uploaded with the data (GIS). Data is processed, recorded, and connected to a map via GIS.
3.Making use of AR in the map. The current utilities are shown as 3D objects. This gives workers on-site information on the precise placement of pipes and lines.
4.Using a tablet or phone screen to access the info. To determine where it is safe to dig, users simply need to point the device downward towards the earth. Instead of looking for it on paper maps, which may be obsolete or erroneous, off-site personnel may access all the information they require about the location of utilities on the maps.
Therefore, utility mapping using augmented reality aids to save time and steer clear of expensive errors and delays. With computerized maps, operators will always be aware of the location of utility lines, and preventing damage to the wires.
Utility firms find the technology appealing due to these advantages, and they are now actively beginning to embrace AR. The energy sector's global AR industry is expected to expand, and according to experts in 2023 the sector will globally ship 20% of all AR hardware.
AR to Coordinate Staff Training
The US Department of Energy research states that by 2027, 25% of US workers in the electric and natural gas utilities will be retiring. The loss of institutional knowledge is the biggest issue facing the utilities business. This workforce is difficult to replace since entrants lack the appropriate technical knowledge and training. Therefore, a lack of employees results in financial losses, decreased productivity, and a company's ability to expand. Businesses are looking for ways to enhance their training procedures in order to combat this.
Companies typically plan their training in-person. This implies that knowledgeable engineers lead training sessions with trainees on the job. However, the lack of manpower is making this more difficult. These meetings require time, and they divert professionals from their primary responsibilities.
AR training can enhance the learning experience. Professional engineers are not required for the real-time, immersive teaching that is possible thanks to technology. Junior engineers can do independent research using pre-drawn AR programs.
An example of implementing interactive training for new hires:
An AR solution is provided by a software start-up called NSFLOW to quicken onboarding and training. Digital workflows and remote support are its two elements. The first module aids in the development of interactive instructions, training, and service procedures. The second is in charge of establishing connections between your field technicians and distant experts.
The platform is used by DTE Energy in the US to develop engaging training programs and handbooks for new hires. The platform is available for self-study by newcomers. This type of AR instruction is conducted without an instructor present.
Real-time calls allow new hires to communicate with specialists who are stationed far away. In the new technician's AR glasses, the specialists can see photos from the cameras. The expert can then instruct the pupil and provide technical guidance at that point. All onboarding and training sessions are now simpler and more practical as a result. Professional specialists, in turn, don't have to invest as much time on travel and offline meetings. They can instead concentrate on their own tasks.
Advantages:
1.Cheaper onboarding and training. Managers can make a course available to all of their staff members after it has been created. Tutors and training materials are not subject to additional fees.
2.There's no requirement for the instructor to be present in person. Almost all courses can now be taught virtually, thanks to augmented reality.
3.Saving time. Experts benefit greatly from AR remote support since it allows them to service more clients per day while traveling less. Additionally, it means that younger staff won't have to wait for them, or cause work halts.
AR to aid Equipment Maintenance
3% of working days are wasted annually in the US energy sector due to malfunctioning equipment. Although this might not seem like much, it results in $30 million losses for each company. Consumers of energy may also be impacted because malfunctions in electric equipment might result in blackouts that can completely shut down a whole city.
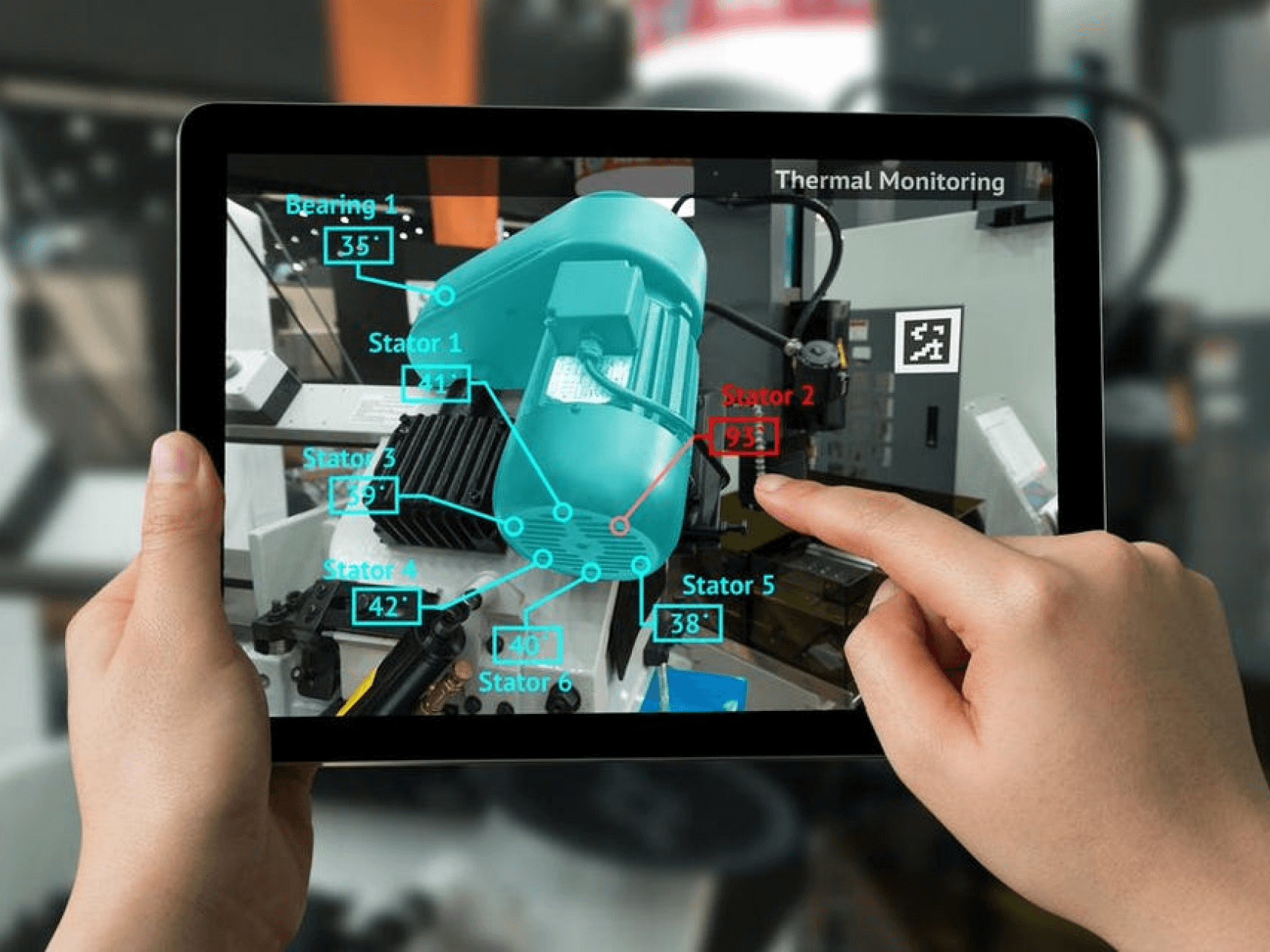
Asset maintenance is one of the most exciting applications of AR. A specific range of issues can be resolved more efficiently and effectively thanks to the ability of AR technology to superimpose a 3D model on a piece of machinery in real time. Field technicians are empowered to instantly access operational paperwork, revealing the asset type, maintenance history, or replacement circumstances using AR mobile devices or smart glasses.
This enables a lineman to act quickly in the event of any broken equipment by placing an order for a replacement or dialling a repairman. The introduction of augmented reality solutions into the energy and utilities sector dramatically speeds up operational procedures and saves money and time.

An example from real life maintenance of utility equipment:
Recently, Xcel Energy Inc., a Minnesota-based company, experimented with AR in its routine maintenance tasks. Their objective was to streamline procedures, make them go more quickly, and reduce errors. Operators may study user manuals for any maintenance operation using AR and video call distant specialists. Additionally, they have easy access to the whole maintenance history that has been documented. The result was a 60% reduction in downtime for the business.
Advantages:
1.Faster equipment maintenance. Businesses may cut the time spent on maintenance in half with AR.
2.A decrease in human error. Engineers may now perform precise calculations and make predictions thanks to technology. It brings down error rates by 33%.
3.Higher fix rates. Technicians may share 3D renderings with distant experts and buy spare components using augmented reality. Fix rates are raised by 20% as a result.
AR to Increase Safety and Health
AR helps to increase operational safety and streamline oil and gas electronics project management by allowing employees to simulate subsurface assets and large machinery with AR equipment to anticipate any future issues.
Field technicians can identify and address hazards caused by broken equipment by using connected AR glasses, which they wear while working. Utilizing augmented reality technology, the implementation of safety rules can be seen in real time on the ground, enhancing both productivity and workplace safety.
Under difficult circumstances, energy specialists operate. They first use risky and dangerous machinery and tools. Risks include being ran over by a large machine, getting trapped between moving pieces, or being harmed by poisonous equipment fumes. Second, they frequently perform their jobs at high altitudes in challenging locations. This raises the possibility of falling and suffering an injury, especially for those with little to no expertise.
Risk areas can be mapped using AR technology. Engineers can avoid problematic locations by using smart glasses to identify danger zones and provide a full description of them. Additionally, safety rules and instructions can be displayed on AR glasses, instructing personnel on how to work in hazardous situations. As a result, accidents are reduced.
If a condition worsens quickly, engineers could require immediate assistance. Engineers may be able to video call knowledgeable professionals thanks to AR solutions. This quick access to assistance lowers the possibility of workers fixing equipment incorrectly. Less people will need to travel to dangerous, challenging regions as a result of these conversations. Businesses can maintain the safety of their employees and save money on sick leave compensation and staff replacement as a result.
An example from real life improved worker safety:
Siemens Energy has been utilizing augmented reality to link their on-site employees with remote experts since 2020. The business found it challenging to efficiently maintain and regularly inspect its equipment. Risks to workers were present since this job was done in difficult-to-access locations.
Siemens engineers can remotely check, treat, and repair their industrial equipment using augmented reality. Faster resolution times and more productivity are the results. Additionally, it improves worker safety because Siemens Energy was able to cut down on accidents and injuries by 43%.
Advantages:
1.Improved safety. By using AR, employees may complete jobs without facing any genuine risk.
2.Fewer accidents. Companies can drastically lower the number of injuries by implementing AR because employees won't have to travel to challenging locations.
3.Cost reductions. Costs are controlled because there are fewer accidents and fewer trips.
In conclusion
The utility and energy industries were thought to be hesitant to accept disruptive innovations. They have relied on conventional, non-digital methods of finishing their activities for many years.
But as time goes on, it’s worth noting that more and more companies are beginning to use AR in their operations. Some businesses are utilizing technology to improve the effectiveness of worker training. Others are planning upkeep of equipment more economically. Additionally, AR can enhance worker health and safety.
What sectors use augmented reality?
AR spans sectors like healthcare for surgeries, retail for virtual fittings, education for enriched learning, real estate for property tours, and automotive for navigation. It's also pivotal in manufacturing, entertainment, and tourism, elevating user experiences, training, and efficiency.
What is the benefit of augmented reality in industry?
AR in industry boosts efficiency, safety, and training by overlaying digital data onto reality, aiding visualization and real-time decisions. It cuts errors, quickens training, offers virtual prototypes, and gives immediate data access, resulting in cost savings and heightened productivity.
Is augmented reality needed in oil and gas?
AR in industry overlays visual instructions on equipment, facilitating remote expert collaboration with on-site workers. By illustrating intricate data, it minimizes errors, hastens inspections, and quickens decisions, enhancing efficiency and saving costs.