The toughest choice in everyone’s life:
DC or Marvel
Coca-Cola or Pepsi
Cats or dogs
Or maybe even pineapple on pizza?
But seriously, we want to discuss one of the most debated and relevant topics: iPhone vs Android user behavior. Why is this important, and what does it mean?
We have made this material as useful as possible for specific target groups looking for practical insights for their tasks. Whether you are a marketer, analyst, mobile app developer, business owner, startup founder, or investor - you will find all the answers here.We will explore iOS vs Android differences, analyze which platform is worth investing in, and assess the risks and opportunities related to user behavior and mobile app user engagement.
Understanding the smartphone divide in 2026
Android market share (as of the end of 2025) stands at ~72%, while iPhone (iOS) market share for the same period is ~28%. These numbers are relatively stable, fluctuating within a range of no more than 5-7%.
And at first glance, it seems like there is no real competition — one platform is nearly 2.5 times more popular. If this were a debate about food or personal preferences, the answer would be obvious.
However, in this case, another parameter is far more important: in-app purchases. iPhone vs Android divide is striking here as well, but in the opposite direction. Apple App Store users generated about $138 billion in revenue in 2025, compared to about $80 billion spent by Android Market users.
Surprise! After App Store revenue comparison, the picture has dramatically shifted. Hasn’t it?
Moreover, when analyzing Mobile app revenue, we must also consider global consumer spending. Last year, this figure reached an estimated $150 billion in in-app purchases and paid apps alone (2024 data) across both platforms — and total mobile app revenue industrywide grew to hundreds of billions of dollars in 2025.
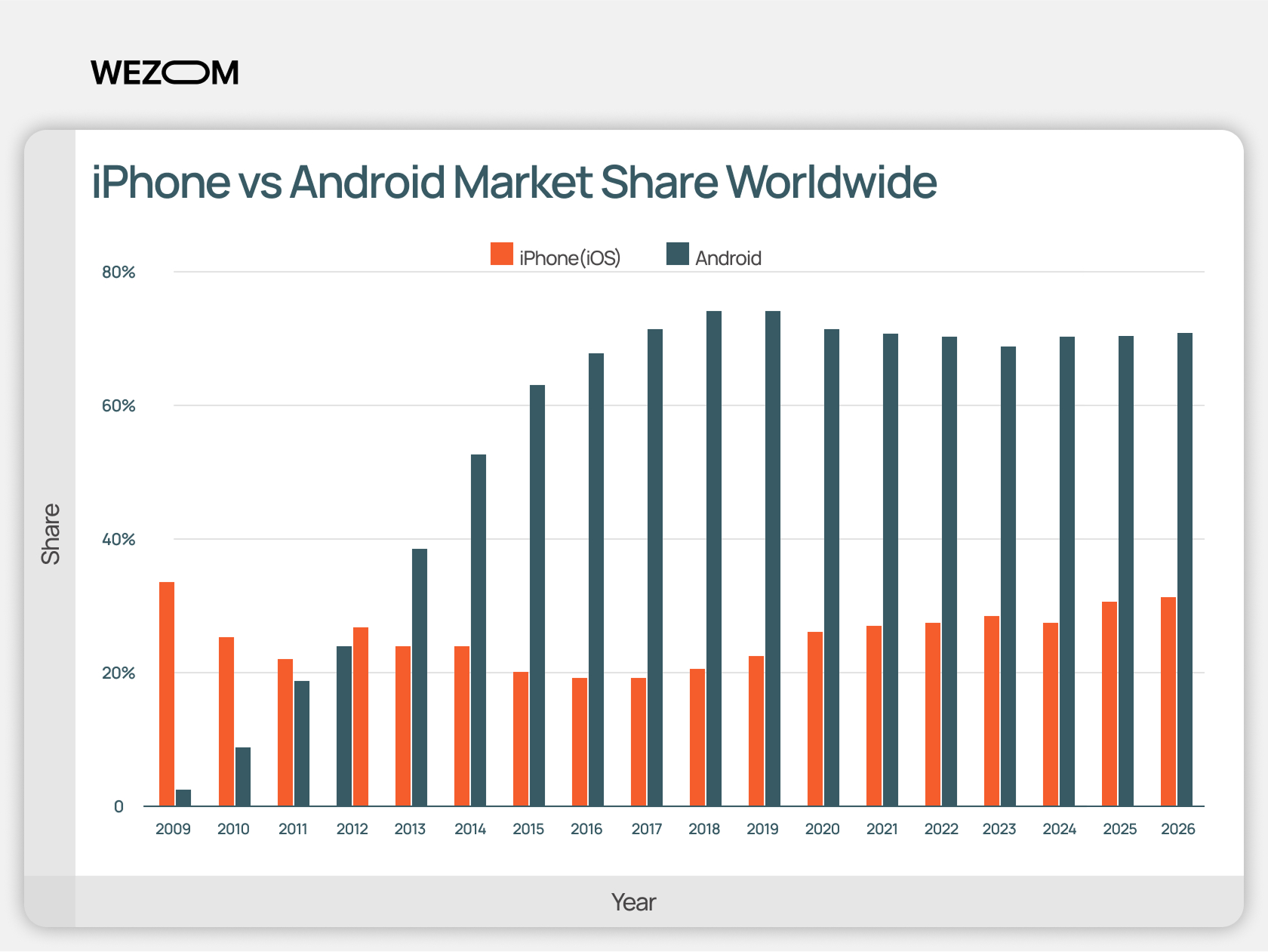
So, what other conclusions can we draw? Growth in Android users has slowed in developed countries but continues in emerging markets like India, Africa, and Southeast Asia.
Meanwhile, iOS market share has seen minor growth in recent years. This is largely due to the launch of more affordable models (such as the iPhone SE) and the expansion of Apple’s ecosystem (Apple Watch, AirPods, services), which helps retain users.

The Key Differences Between Android vs iPhone Users

"Why pay twice as much for a phone that you can’t even customize properly? My Android does everything I need and more. I’ve installed LineageOS, have full control over the system with root access, and love tweaking custom icons and fonts."
© a member of the Wezom development team
"For me, the differences between Android and iPhone are primarily about performance. My smartphone runs without lags or crashes, and I don’t have to spend time fixing settings or troubleshooting errors."
© an employee at Wezom
Android user vs iPhone user debate is endless. And it seems they will never reach a consensus. But we are not here to judge. Our goal is to make one of the most critical decisions in mobile app development - conducting a mobile platform comparison.
This choice impacts EVERYTHING - the target audience, development costs, monetization, technical capabilities, and long-term app support.
It’s essential not just to understand what is the difference between iPhone and Android from a software perspective but also to grasp the key distinctions between users, ecosystems, and app stores on these platforms.
User demographics: Who prefers iPhones and why?
User demographics reflect not only differences in preferences but also socioeconomic, cultural, and technological factors.
This is crucial to determine whether your target audience is ready for consumer spending on Apps.
According to analyst Horace Dediu, the average monthly spending of iPhone users in the U.S. is about $11.2, while Android users spend only about $1.7 per month. In other words, Apple users not only make more in-app purchases but are also willing to spend more.
At the same time, Android app development vs iOS app development can differ significantly. The key reasons lie in technical, market, and organizational aspects, which we will discuss below.
For convenience, let’s present iPhone vs Android user demographics in the form of a table.
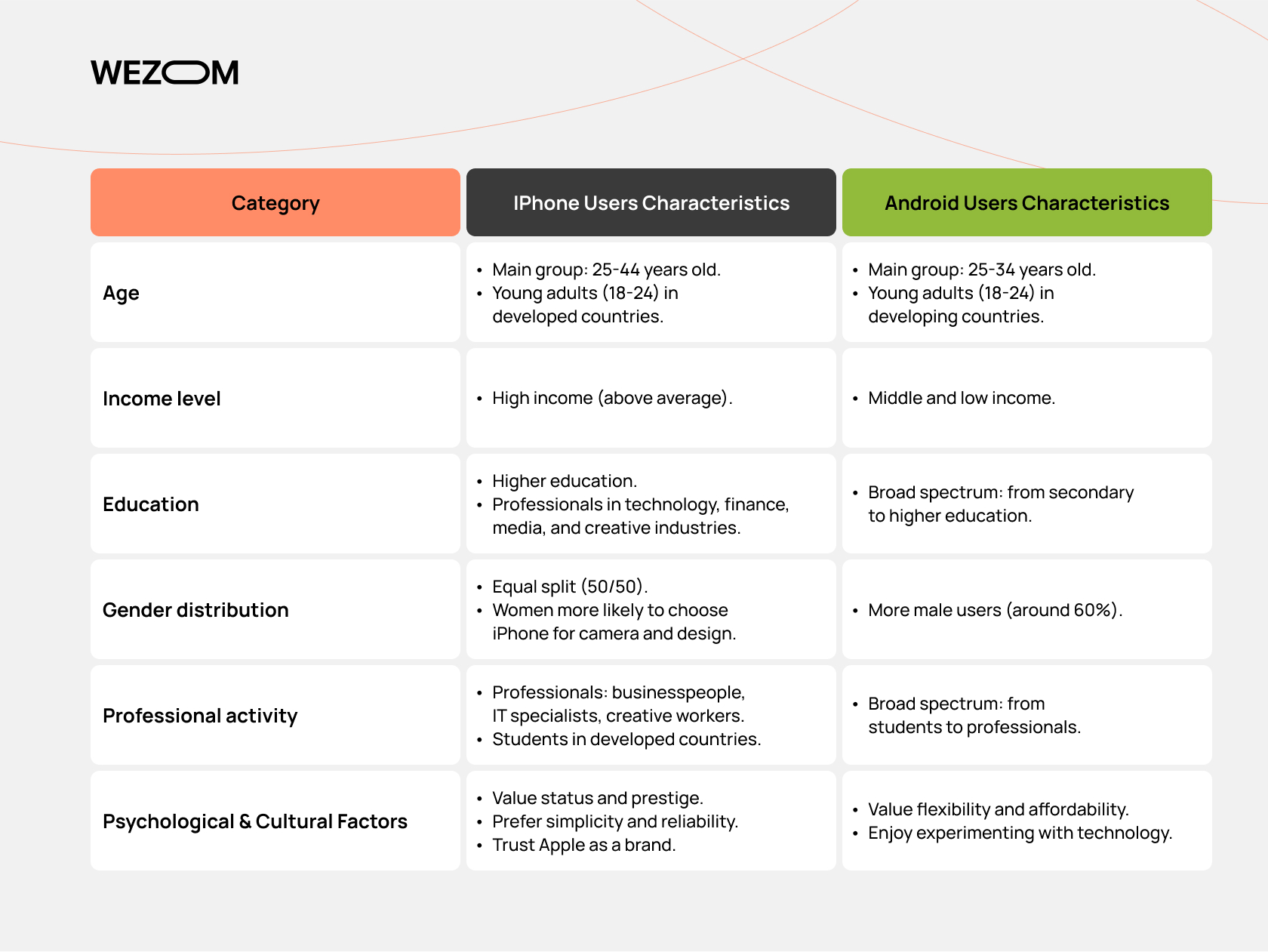
Key regions where iPhone and Android dominate. iPhone users are mostly from the USA, Japan, Western Europe, and Australia — a regional distribution that has remained largely unchanged in recent years. By the way, it is in the USA that Apple products hold a record share. If you were wondering what percent of cell phones are iPhones, we have the answer — about 59% as of 2025–2026. Common reasons for this choice include:
- Cultural preference;
- Easier integration with local services;
- High income levels.
The percentage of iPhone users vs Android differs significantly in developing countries (India, Africa, Southeast Asia, Latin America). Android is also #1 in South Korea and China. Reasons for this include:
- Dominance of local brands (Samsung, LG);
- Patriotic preferences;
- A wide range of devices.
iPhone and Android demographics provide answers to many questions. However, let's dive even deeper into the topic.
User Experience: iOS vs Android
How much do iPhone vs Android features differ? Globally, not much. Both are systems that allow the user to manage their smartphone. However, there are certain criteria by which owners choose their devices. Let's take a look at the main ones.
- Ease of use. iPhone users often note that iOS "just works." The interface is intuitive, and the settings are minimal. This makes the smartphone an ideal choice for those who don’t want to spend time learning technical details.
At the same time, the Android operating system offers more freedom. But this can be both a plus and a minus. Some believe that the setup requires more time and effort. "It’s like a constructor: you can make everything how you want, but you need to spend time."
- Stability. The main differences between iPhone and Android are that statistically, iOS rarely crashes, and updates arrive on time and work smoothly. For Android, stability depends on the device and manufacturer. On older or budget models, lag may occur, and updates are often delayed.
- Software design and user interface differences. Apple adheres to the principle "less is more." The interface is clean, with an emphasis on convenience and intuitiveness. All iOS apps look and work similarly, creating a sense of unity. Overall, the design focuses on making content (photos, text, videos) the centerpiece while keeping the interface unobtrusive.
Android apps allow developers and users to experiment with the interface. Moreover, it adapts to different devices, screen resolutions, and forms (for example, foldable phones). Google uses Material Design, which combines realistic shadows, animations, and bright colors.
- Camera. Apple’s camera is praised for consistently high-quality photos and videos, even without additional settings. Selfies are especially valued. Android cameras often offer more technical features (such as zoom or macro shooting), but the quality depends on the manufacturer.
- Notifications. Even push notifications on Android and iOS come through and feel differently. On iOS, they are grouped in the Notification Center, which can be accessed by swiping down. On Android, notifications are more flexible - they can be grouped, collapsed, or quickly responded to. They support more actions (such as quick replies or media control).
- Security. iPhone security vs Android security differs in terms of vulnerability. iOS users trust the system's security. The App Store is strictly moderated, reducing the risk of malicious apps. Apps from Google Play are also moderated, but the system is more vulnerable to viruses and malware, especially if the user installs apps from third-party sources.
- Durability and support. iPhones receive updates for 5-6 years, making them quite durable. Users appreciate that their devices remain relevant. Support for Android devices depends on the manufacturer. Many devices stop receiving updates after 2-3 years.
App Ecosystem: iPhone vs Android
Apple has created one of the most closed yet convenient ecosystems. All devices (iPhone, iPad, Mac, Apple Watch, AirPods, HomePod) work as a unified system.
Main benefits:
- Seamless integration: Handoff, AirDrop, Continuity allow easy switching between devices. For example, you can start writing an email on the iPhone and continue on the Mac.
- Exclusive services: iMessage, FaceTime, iCloud, Apple Pay, Apple Music — work only within the ecosystem.
- Control: The closed iOS ecosystem reduces the risks of hacking and viruses but limits customization.
- Difficulty of transition: Apple deliberately makes it difficult to exit the ecosystem — moving from iPhone to Android will be painful due to service incompatibility.
Android offers a more open system with a wide variety of devices and manufacturers (Samsung, Google, Xiaomi, OnePlus, etc.).
Main benefits:
- Android user customization: You can change the interface, install third-party apps, and use alternative app stores.
- Unlike Apple, you can choose a smartphone in different price categories with different specifications.
- Google services: Google Assistant, Drive, Photos, Chrome work on any device and are not tied to a brand.
- Transition between devices from different manufacturers is less painful.
The App Store vs Google Play Store
As of the time of writing, there are over 1.3 billion active Apple devices and about 3.6 billion smartphones, tablets, and other devices running the Android operating system worldwide.
It is also interesting that the Google Play Store (as of late 2025) hosted around 3.4 million apps, reflecting the size and openness of the Android ecosystem. The App Store, in comparison, offered approximately 2.1 million apps, indicating a more curated but still extensive app marketplace.
Speaking of mobile app development, monetization should also be mentioned. For instance, Apple takes a 30% commission on sales (15% for small developers), which makes development more expensive. Though, wait, someone might point out that Google also takes a 30% commission. But here, developers have the option to implement alternative payment methods.
And continuing this topic, let's discuss iOS vs Android development costs.
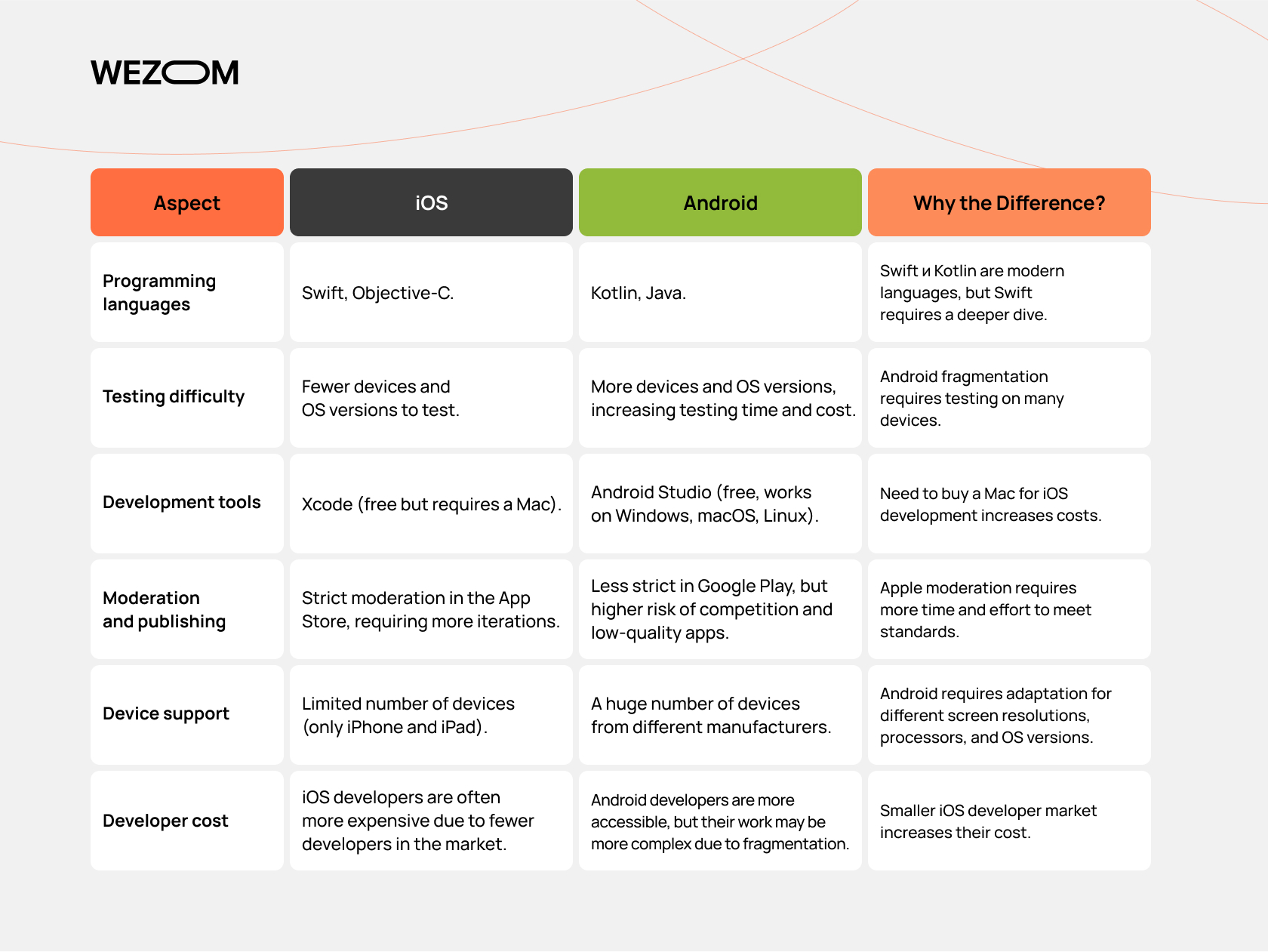
Conclusion: iOS offers more polished, secure, and optimized apps (thanks to strict requirements and enhanced moderation). Meanwhile, Android provides a larger variety, but with a risk of lower quality and fraudulent apps. An alternative option is to consider cross-platform app development.
Customer loyalty iPhonevs Android
In general, Android vs iPhone loyalty is a separate topic. Apple has a very high loyalty rate (over 90%). This means that fans almost never “cheat” on their favorite operating system.
Unfortunately, we couldn't find detailed global statistics, but we can share a sample of stories from the Wezom team:
- 80% of iOS users have never switched to another operating system after their first iPhone purchase.
- 12% of respondents tried Android but returned to iPhone. Only 8% remained on the new platform and don't plan to switch.
- 54% of respondents buy a new phone model every year as it is released, 22% buy one every two years, and the rest do so every three years or less.

User retention for iPhone vs Android is also characterized by emotional attachment. iPhone users often see their devices as an extension of their personality. This is related to the Apple cultural phenomenon, which is actively supported through marketing, media, and the brand's popularity among celebrities.
Android users are less loyal but value the platform's diversity, flexibility, and affordability. Some of them switch to iPhone, especially if their income or status rises.
Integration of hardware and software
Smartphone performance depends on a combination of processor, operating system, app optimization, and ecosystem solutions. iPhone and Android smartphones have different approaches to hardware, which affects their speed, stability, and longevity.
For instance, Apple uses Silicon processors (A-series) – chips designed specifically for their devices. These provide high performance and energy efficiency. The latest processors (such as the A18 Pro) outperform competitors in speed and power tests. Moreover, Apple designs its operating system with its processors in mind, allowing smartphones to run smoothly even 5–6 years after release.
In contrast, Android offers a vast range of devices from different manufacturers (Samsung, Google, Xiaomi, OnePlus, Oppo, etc.), which gives users more options but leads to fragmentation.
Android smartphones use chips from Qualcomm (Snapdragon), Samsung (Exynos), MediaTek, and Google Tensor, meaning different models have varying performance levels. Yes, users have a choice in budget: from super-economy (under $120) to ultra-premium ($1800+, especially foldable models).
By the way, when we talk about high customization, it also means the possibility to change the battery (in some niche and rugged models), expand memory with microSD cards, and choose different form factors (foldable screens, gaming models, etc.).
The Future of iPhone vs Android: Predictions for the smartphone wars in 2026
The smartphone industry has been divided into two camps for over 15 years, and neither has become a 100% winner yet. Android vs iPhone users worldwide will never give in to each other.
Let’s take a look at the present and near future and explore the trends and technologies that are shaping the power balance in 2026.
Foldable Smartphones or Classic?
Apple users vs Android often argue about form factor. And now they finally have a reason for this debate. Apple is expected to introduce its first foldable iPhone in 2026, staying true to its strategy of entering the market later, once the technology matures. Meanwhile, Android already has clear leaders in the foldable devices category: Samsung (Galaxy Z Fold/Flip) and Google (Pixel Fold). By 2026, foldable smartphones have become more affordable and more reliable, which continues to give Android devices an advantage in this segment.
Performance and Chips: Who's Faster?
iPhone vs Android usage is also an eternal debate about power and performance. In 2024, Apple introduced the A17 Pro processor, followed by the A18 Pro in 2025, delivering notable gains in efficiency, GPU performance, and on-device AI processing. These chips continue to outperform most competitors in single-core performance and power efficiency.
Meanwhile, Android uses processors from Qualcomm (Snapdragon), Samsung (Exynos), and Google (Tensor). Snapdragon 8 Gen 4 (Elite) brings major improvements in AI acceleration and energy efficiency, narrowing the gap with Apple and making flagship Android devices more competitive than ever.
Artificial Intelligence: Caution vs Active Implementation
Google continues to actively integrate AI into Pixel smartphones, utilizing Google Assistant, Magic Eraser, generative photo and video tools, and on-device AI features. By 2026, AI autonomy and on-device processing have become core differentiators for Android devices. Apple, while more cautious, has significantly expanded AI capabilities through iOS 18 and iOS 19, focusing on privacy-centric on-device neural processing for photos, videos, system automation, and voice interactions.
Android and iPhone market trends indicate steady stability. As of 2026, no dramatic shifts in global market share are expected, and neither platform shows signs of losing its dominant position. Instead, competition continues through incremental innovation rather than disruptive changes.
Final thoughts on choosing between iPhone and Android in 2026
The smartphone war won’t end in 2026, but Android will continue to dominate in terms of user numbers, while iPhone will maintain its lead in profitability and user loyalty.
Which platform is best for app development?
iOS is ideal for monetization since users are more likely to pay for apps and in-app purchases. It is a closed ecosystem with high user loyalty, but development requires strict adherence to App Store rules.
The number of iPhone vs Android users clearly tilts in favor of the “green robot.” Android covers far more users worldwide, especially in developing countries. It is an open platform with flexibility for customization but requires adaptation to a wide range of devices and OS versions.
If you want to create an app that will succeed on both platforms, reach out to us! We are a company with vast experience. Our team will help you choose the best strategy, develop a high-quality product, and bring it to market. Trust the professionals, and we will make your app popular!

