Not every team needs micro apps. If your business runs on a few core platforms and rarely changes workflows, a traditional all-in-one mobile app might be enough. But for enterprises juggling multiple systems, shifting priorities, and a growing demand for mobility — micro apps are not just useful, they’re transformative.
"The future of enterprise apps isn’t big. It’s small, fast, and focused."
Gartner, Mobile App Trends Report 2025
Micro apps are lightweight, purpose-built tools that do one thing exceptionally well: update a delivery, approve a request, log a shift. They’re fast to build, easy to use, and integrate seamlessly with enterprise systems like ERP, CRM, and HRIS. As organizations decentralize and employees expect consumer-grade experiences from business tools, micro apps are filling critical gaps with minimal friction.
This article explores why forward-thinking enterprises are investing in modular mobile apps, how they fit into broader IT strategies, and what it takes to build them right.
Micro Apps: What They Are and Why Enterprises Are Embracing Them
Micro apps are modular, task-specific mobile tools that serve a single function or workflow. Think of them as the opposite of all-in-one apps: instead of packing in every possible feature, a mobile app for one feature zeroes in on one core task. For example, an approval workflow app for HR might let managers review and approve leave requests on the go — without having to log into a bulky enterprise system.
Unlike full-feature mobile apps, which often mirror desktop software, micro apps focus on solving a specific problem quickly. They are typically developed using lightweight frameworks and connect to backend systems via APIs. This makes them fast to build, easy to deploy, and highly adaptable to specific team needs.
Micro apps are often part of a broader app unbundling strategy, where large applications are split into smaller, modular services. This modular approach aligns perfectly with agile enterprise environments and evolving user expectations.
Furthermore, micro apps promote a culture of continuous improvement. Since each app serves a narrowly defined function, it’s easier to gather feedback and iterate quickly. Organizations can refine processes on the fly, releasing updates or new micro apps without disrupting existing workflows.
Key Benefits of Micro Apps for Business
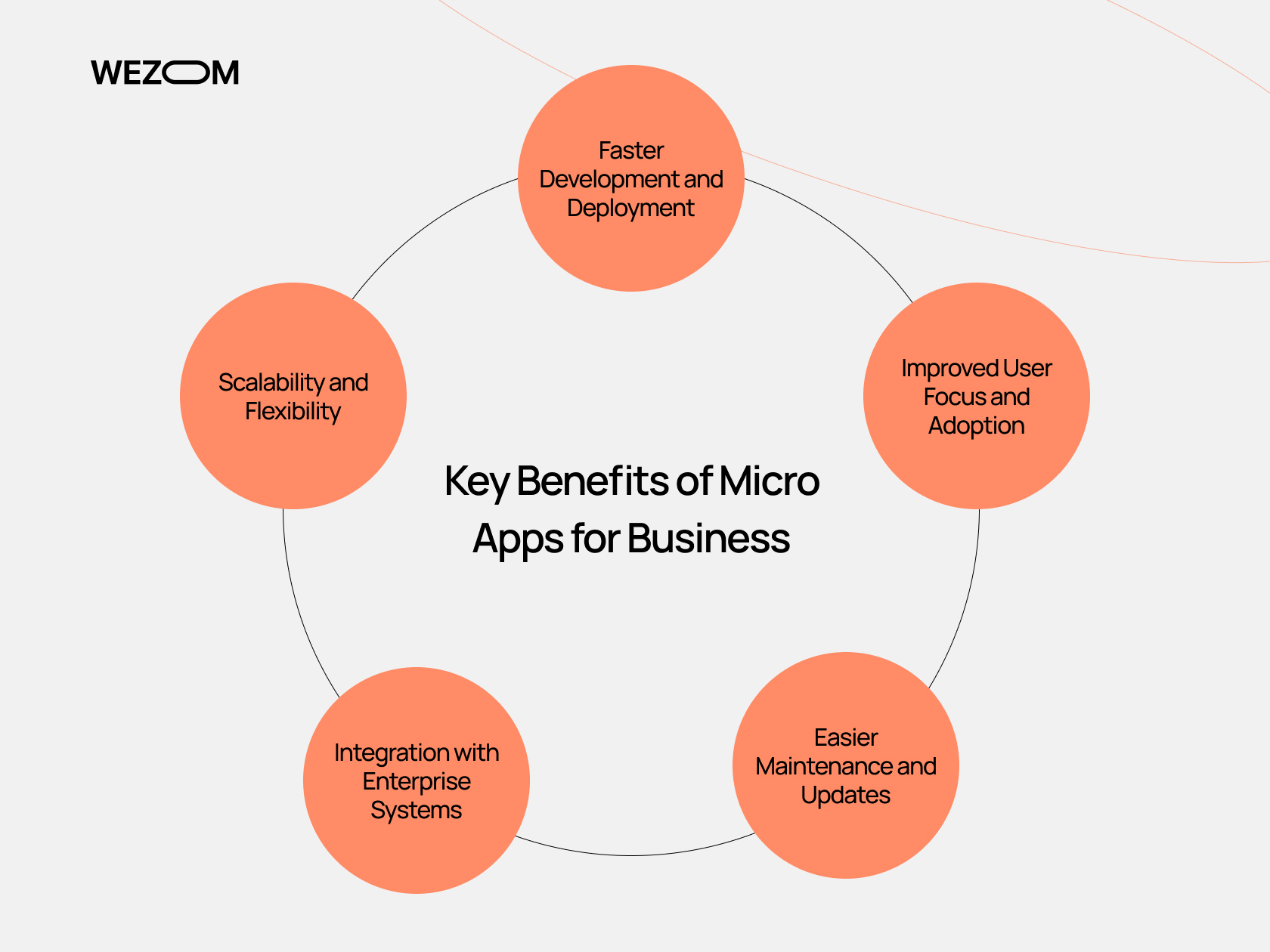
Faster Development and Deployment
Because they’re smaller in scope, micro app development can be completed and released in weeks, not months. Teams can focus on one workflow at a time, reducing complexity and allowing for faster time-to-value. This speed is particularly advantageous in fast-moving industries like logistics, finance, and healthcare.
Improved User Focus and Adoption
With a narrow focus, micro apps reduce user friction and learning curves. Employees can launch an app, complete a task in seconds, and move on. This task-based design boosts engagement and encourages adoption. Instead of overloading users with options, the interface is clean, purposeful, and intuitive.
Easier Maintenance and Updates
Since each micro app handles a single function, updates are simpler and carry less risk. There’s no need to retest an entire system just to fix or improve one component. This leads to lower maintenance costs and less downtime for users.
Integration with Enterprise Systems
Micro apps are built to fit into the larger enterprise ecosystem. They connect to existing tools like ERP, CRM, or HRIS via APIs, allowing companies to extend core functionality to mobile in a lightweight way. This supports a modular mobile apps strategy that enhances, not replaces, enterprise platforms. The result is a cohesive digital workplace where tools work together harmoniously.
Scalability and Flexibility
As business needs evolve, micro apps can be added, modified, or retired independently. This scalability means organizations can respond to new requirements: whether regulatory, operational, or technological, without overhauling entire systems. It also supports experimentation, allowing teams to test innovative features without high stakes.
When to Use Micro Apps vs Full-Feature Mobile Apps
| Factor | Choose Micro App | Choose Full-Feature App |
| Scope | Single task or workflow | Multiple complex features |
| Budget | Limited development resources | Larger investment available |
| Time-to-Market | Need to launch quickly | Longer timelines acceptable |
| Audience | Specific roles or teams | Broad user base |
| Integration Need | Extending existing systems via APIs | Building standalone functionality |
Use micro apps when you need workflow-specific mobile solutions that support internal processes with minimal overhead. They’re ideal for task-based apps for teams and rapid iterations.
It’s worth noting that micro apps don’t replace traditional apps entirely. Instead, they fill in the gaps, offering streamlined access to specific functionalities while maintaining alignment with broader systems. This hybrid strategy ensures optimal coverage and usability across all user touchpoints.
Real Micro Apps Examples in Action
- Field Service App for Delivery Updates: Logistics staff can update delivery status in real-time through a simple mobile interface connected to the ERP.
- Internal Expense Reporting Tool: Employees upload receipts and submit expense forms from their phones. The app validates data and routes it for approval. This kind of app is a perfect example of internal business tools.
- B2B Sales Enablement Micro App: Sales reps access product catalogs, pricing, and client documents while on the road, integrated with the CRM.
- Healthcare Shift Scheduling App: Nurses and staff can check schedules, swap shifts, and confirm attendance without navigating complex systems.
- Onboarding Checklist App: New employees complete required tasks (submitting IDs, signing documents, watching videos) through a guided mobile experience, integrated with HR systems.
These examples highlight the role of micro apps in business as lightweight, focused solutions that improve efficiency and responsiveness.
How to Develop and Deploy Micro Apps
.jpg)
Choosing the Right Framework and Backend
Many teams opt for cross-platform solutions like Flutter or React Native to streamline development. Low-code platforms also enable faster prototyping. When speed and customization must go hand-in-hand, frameworks that support reusable components and modular architecture are key.
API-First Approach for Integration
Integration is key. A successful micro app architecture depends on reusable APIs that connect to enterprise systems while maintaining data security. RESTful or GraphQL APIs enable apps to retrieve and update data in real-time. API gateways can also manage traffic, logging, and rate limits.
Security and Access Control
Since micro apps often touch sensitive business data, role-based access control (RBAC), secure authentication, and encrypted data transmission are essential. Following best practices ensures compliance without slowing down development. Use OAuth2, SAML, and multifactor authentication to keep user sessions secure.
Deployment Strategies
Micro apps can be distributed via enterprise app stores, mobile device management (MDM) platforms, or embedded into existing employee portals. Clear onboarding instructions and user training further enhance adoption.
Challenges to Consider
- Risk of Fragmentation
With multiple micro apps in circulation, businesses must manage a growing portfolio without overwhelming users. Clear naming, consistent branding, and centralized management help mitigate this. Some companies build internal marketplaces where employees can find and download micro apps relevant to their role.
- Ensuring Consistent UX Across Micro Apps
A unified user experience is key to adoption. Design systems and reusable UI components help maintain visual and functional consistency across apps. When possible, follow existing corporate branding and interface patterns to reduce cognitive load.
- Managing Multiple Codebases
Each micro app may have its own codebase, which can complicate updates and QA. Consider shared components or a common framework to reduce duplication. Automation tools for testing and CI/CD can help manage the complexity.
- Governance and Compliance
As the number of apps grows, maintaining compliance with internal policies and external regulations becomes critical. Establish a governance model early, defining who can create micro apps, how data is handled, and how apps are monitored over time.
Conclusion
In today’s dynamic enterprise environment, micro apps offer a focused, flexible alternative to traditional mobile applications. By delivering lightweight business apps tailored to specific workflows, businesses can boost productivity, improve adoption, and move faster. Whether it’s a simple approval tool or a sales dashboard on the go, micro apps are proving that smaller, smarter solutions can drive big results.
Companies investing in enterprise productivity apps will find that micro apps deliver excellent ROI through targeted, efficient performance. As micro apps mature, expect to see tighter integration with AI, voice interfaces, and context-aware experiences: opening the door to even more intelligent and personalized tools. The future of enterprise mobility is modular, agile, and increasingly micro.