Ever notice how your power goes out and it feels like the entire neighbourhood is in the dark? Or how you get that electricity bill and wonder where all the energy went? Yeah, I know the feeling. The thing is, our power grids (the networks that deliver electricity to our homes and businesses) are basically running on technology from decades ago. And honestly, it's not cutting it anymore.
That's where smart grid technology steps in. It's not some sci-fi concept. It's real, it's being deployed right now, and it's about to change how we use, distribute, and think about electricity.
So, what’s the smart grid meaning in simple terms?
A smart grid is basically an upgrade to the traditional power system. Old grids are one-way streets: electricity flows from power plants to your house, that's it. No feedback. A smart grid is different. It's a two-way communication system using digital technology, sensors, and automation to monitor and manage electricity in real-time. Think of it like upgrading from a landline to a smartphone — suddenly you've got way more control.
Here's what makes it "smart": the network detects problems instantly, adjusts power distribution automatically, learns patterns, adapts, and even talks to renewable energy sources. Less waste. More control. Better integration.
Smart meters and sensors track electricity consumption in real-time and monitor voltage, temperature, and flow rates. They feed data through digital communication networks (fibre optics, wireless, cellular) connecting everything like a nervous system.
Software and automation process that data instantly, making split-second decisions: redirect power, activate storage, pull from renewable sources. Excess energy gets stored in batteries, released when demand spikes. Solar and wind variability? Balanced automatically. Sensors → communication → smart decisions → stable, efficient energy flow.
Types of Smart Grid Solutions
Smart grids aren't one-size-fits-all. Different approaches work for different situations:
| Smart Grid Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Microgrids | Smaller, localized grids serving a specific area. Can operate independently or connected to the main grid. Include their own generation, storage, and control systems. | Neighborhoods, university campuses, industrial parks, remote areas. |
| Energy Storage Systems | Battery technology and storage solutions that optimize when to store and release energy based on demand and pricing. EVs act as mobile storage units. | Peak demand management, backup power, cost optimization. |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Smart systems that predict solar and wind generation, balance variability against demand, and integrate large amounts of clean energy seamlessly. | High renewable energy penetration, climate goals, sustainability targets. |
| Demand-Side Management | Influences consumer behavior through pricing signals and automation. Shifts demand to cheaper off-peak hours, reduces peak loads automatically. | Cost reduction, grid stability, consumer engagement. |
Each type addresses specific challenges. Microgrids bring resilience. Storage systems bring stability. Renewable integration brings sustainability. Demand management brings affordability. Together, they make the entire system smarter.
How Does Smart Grid Work?
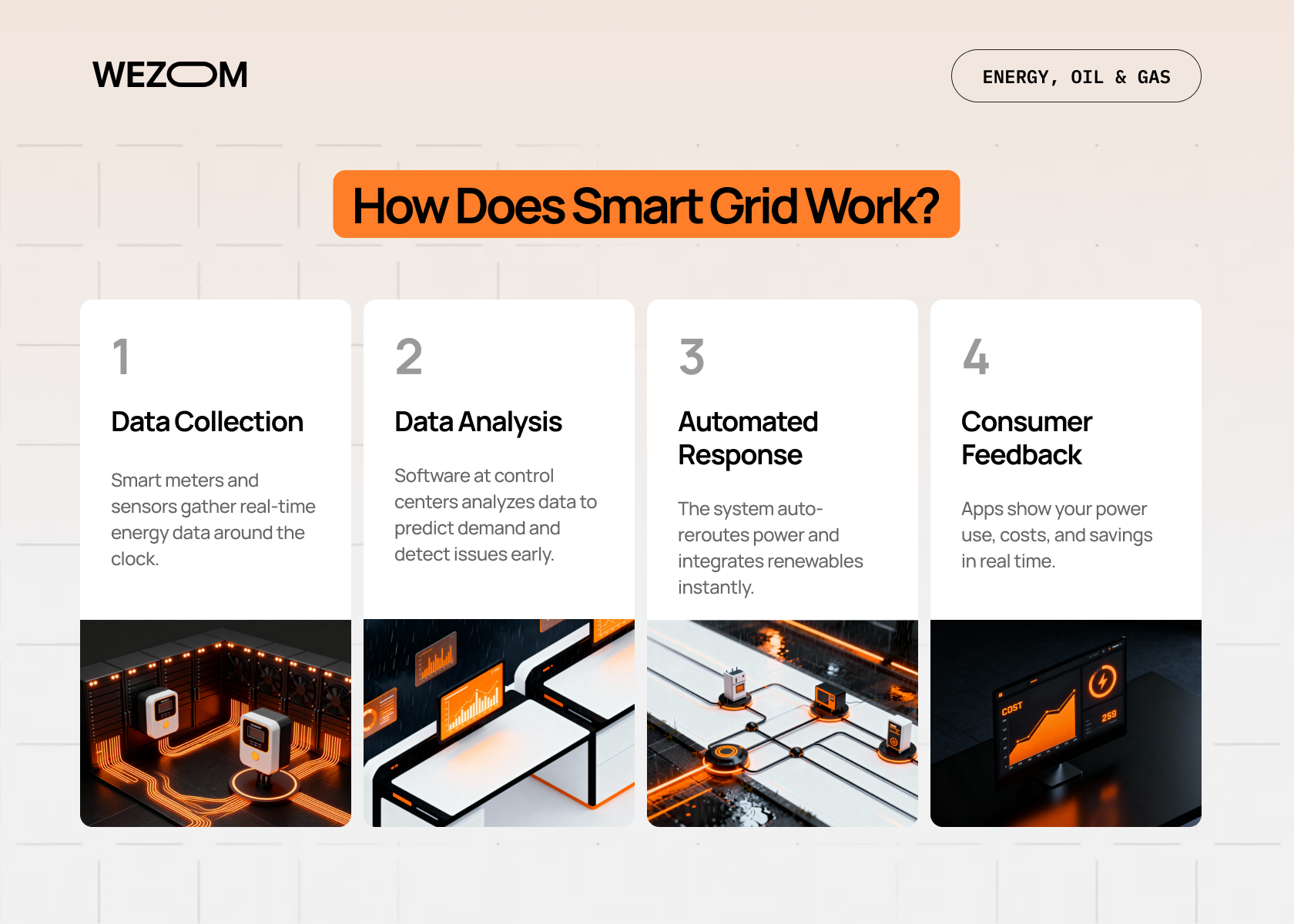
The process sounds complex, but follow along. Here's the workflow:
- Data Collection
Millions of smart meters and sensors gather real-time data about electricity consumption, generation, and network conditions. This happens constantly, 24/7.
- Data Analysis
That massive amount of data gets sent to control centers where software analyzes it. The system detects patterns, predicts demand, spots inefficiencies, and identifies problems before they become failures.
- Automated Response
Based on analysis, the system makes decisions. It reroutes power, activates backup systems, integrates renewable sources, or sends signals to appliances in homes. Automation means this happens instantly, not manually.
- Consumer Feedback
You get information too. Apps and dashboards show your electricity usage, costs, and opportunities to save. You're no longer in the dark (literally and figuratively).
The whole thing creates a feedback loop. The more data collected, the smarter the system gets. It learns your patterns, anticipates problems, and optimizes everything.
Benefits of Smart Grids
Okay, so why should you care? What's in it for you and your wallet?
The global smart grid market was valued at $73.8 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $161.1 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 16.9%.
"Widespread deployment of smart grids is critical for a secure, cost-effective and clean energy future. Smart grids can play a significant role in enabling nearly all clean energy technologies, including renewables and electric vehicles."
© International Energy Agency (IEA)
Here are some of the benefits:
- Reducing Energy Losses
Traditional grids lose about 6-8% of electricity during distribution. Heat, old infrastructure, inefficiencies — it all adds up. Smart grids cut those losses significantly. Real-time monitoring means problems get fixed faster, waste gets eliminated, and more power actually reaches your house.
- Lower Electricity Costs
Less waste means cheaper electricity. Plus, you gain visibility into your consumption. You see when you're using power, and you can shift usage to cheaper times. Some smart grid systems offer time-of-use pricing: pay less during off-peak hours. Could save your household hundreds per year.
- Integrating Renewables at Scale
Solar and wind are great, but they're unpredictable. Smart grids solve that. They can integrate large amounts of renewable energy without destabilizing the network. More clean energy in the mix, less dependence on fossil fuels.
- Benefits for Businesses
Companies get predictable costs, better planning, and the ability to generate and store their own energy. For manufacturers, optimizing electricity use can cut operational costs by 15-20%.
For grid operators? Way easier to manage distribution, prevent failures, and integrate new technologies.
Smart Grid Solutions in the Real World
This isn't theoretical. Companies and governments are implementing this now.
Smart meters are already in millions of homes. They send data automatically. No more manual readings. Some utilities offer apps where you can see your consumption minute-by-minute.
Microgrid projects are popping up everywhere. Islands, remote areas, and even cities are building localized smart grids. Brooklyn has one. So does parts of Germany and Australia.
Renewable integration? Denmark now gets over 80% of its electricity from wind thanks to smart grid technology. The smart system balances all that variable energy seamlessly.
Electric vehicle charging networks are becoming smart too. They communicate with the main grid, charging when there's excess power and holding back when demand peaks.
And home automation? Already here. Your smart thermostat, washing machine, and water heater can all optimize their usage based on grid signals and pricing.
How to Implement Smart Grid: Steps for Companies and Governments
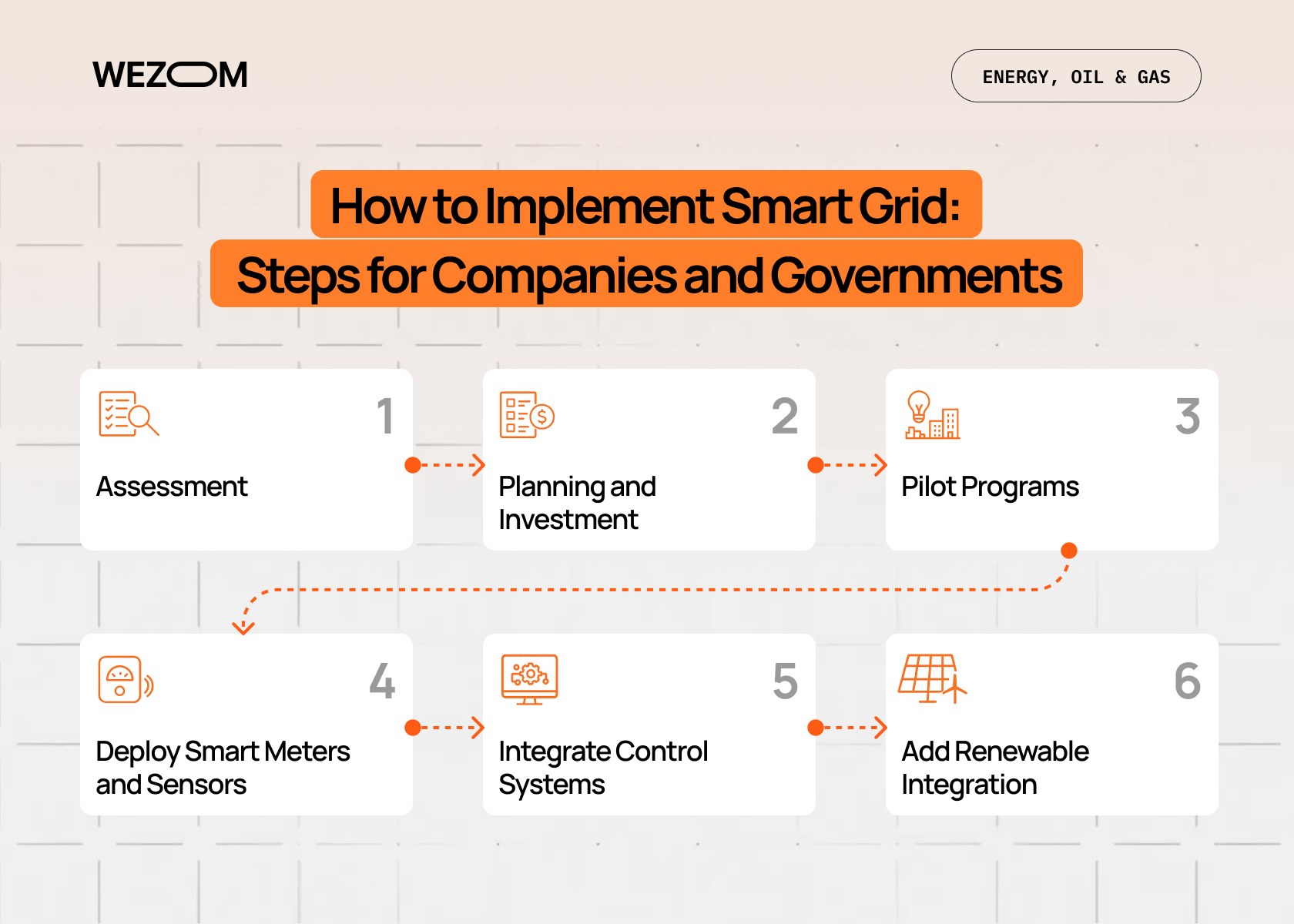
Want to build a smart grid? It's not plug-and-play, but there's a roadmap.
Step 1: Assessment
Evaluate current infrastructure. What's working? What's aging? Where are the biggest inefficiencies? This determines your starting point.
Step 2: Planning and Investment
Decide on smart grid components you'll deploy. Smart meters? Check. Sensors? Check. Storage systems? Maybe. Set realistic timelines and budgets. This is a multi-year project.
Step 3: Pilot Programs
Don't roll it out everywhere at once. Start small: a district, a city section. Test, learn, adjust.
Step 4: Deploy Smart Meters and Sensors
Replace old meters. Install sensors throughout the network. Build communication infrastructure. This is the foundation.
Step 5: Integrate Control Systems
Deploy automation software and digital systems that analyze data and make decisions. Connect everything.
Step 6: Add Renewable Integration
Once the smart system is running smoothly, integrate solar, wind, and storage. The system can handle it.
Conclusion
Transforming your grid into a smart, adaptive, and data-driven system is a competitive necessity.
WEZOM provides end-to-end smart grid implementation: from infrastructure assessment and IoT integration to real-time monitoring systems and renewable energy management.
We combine engineering expertise, digital innovation, and automation to help utilities achieve peak performance, minimize downtime, and meet future energy demands.
Get in touch with our specialists to explore how we can help you deploy a reliable, scalable, and intelligent energy network.

FAQ
What is Smart Grid?
A smart grid is an electricity network that uses digital technology, sensors, and automation to monitor and manage power distribution in real-time. Unlike traditional grids, smart grids enable two-way communication between utilities and consumers, optimize energy use, reduce waste, and integrate renewable energy sources efficiently.
Can Smart Grids help reduce electricity costs?
Absolutely. Smart grids reduce energy losses during distribution, which lowers overall costs. Additionally, consumers get real-time visibility into consumption and can shift usage to cheaper off-peak hours. Many utilities offer time-of-use pricing in smart grid systems, allowing households to save 15–30% on electricity bills.
How does a Smart Grid support renewable energy sources?
Smart grids handle the unpredictability of solar and wind energy. Through real-time data analysis and automation, the system predicts generation, balances it against demand, and uses energy storage to stabilize the network. This allows utilities to integrate large amounts of renewable power without compromising stability.
How does a Smart Grid differ from a traditional power grid?
Traditional grids are one-way systems: electricity flows from power plants to consumers, period. Smart grids enable two-way communication, use sensors and digital systems for real-time monitoring, include automation capabilities, and can integrate renewable energy. They're faster, more efficient, and give consumers visibility and control.
How is user data protected in Smart Grid systems?
Legitimate concern. Most smart grid systems use encryption, secure communication protocols, and regular security audits. Your consumption data is protected under privacy laws in most countries. However, always check your utility's privacy policy and ensure they're compliant with regulations like GDPR (in Europe) or similar local laws.

