One of the main problems in the car transportation business is the lack of timely understanding that the truck becomes unprofitable and minimal repairs no longer help. In this case, it must be replaced entirely with a new one. It is also essential to monitor the condition of the trailers used with the truck. All this can be done using the proper transport management system (TMS).
We have experience in developing such TMS modules that give results. Therefore, we would like to share our knowledge and analyze possible fleet management costs.
The Importance of Fleet Management Cost Analysis
Fleet management cost analysis is critical to make your business truly profitable. Specifically, with proper implementation, it allows you to identify hidden fleet operating costs that can go unnoticed without detailed accounting, including fuel, maintenance, repair, and the others, as well as optimize fleet management processes (for example, through choosing the most economical routes, in-time vehicle maintenance scheduling, making correct decisions about replacing or repairing cars, and so on).
Therefore, cost analysis can be considered an important tool for improving your business efficiency and profitability.
What Goes Into Calculating Total Cost of Ownership?
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is a key aspect of fleet management, as it allows you to determine all the budget on owning and operating vehicles. TCO includes fixed and operating costs, so its understanding provides an opportunity to optimize management processes and make more informed financial decisions regarding the fleet.
Fixed vs. Operating Costs
Fixed and operating costs are the two main categories included in calculating TCO.
| Fixed costs | Operating fleet expenses |
| Vehicle acquisition: It is the initial cost of buying or leasing a vehicle and may vary depending on the vehicle's type, brand, and model. | Fuel: It is one of the largest items, depending on vehicle mileage and fuel prices. Using economical vehicles and optimizing routes can help you save your budget. |
| Insurance: It means regular payments for vehicle insurance that cover risks associated with operation. It can be both mandatory types of insurance and additional coverage. | Maintenance and repair: Regular and routine repairs are necessary to keep the vehicle in good condition. Timely maintenance helps to avoid serious breakdowns. |
| Depreciation: It lies in decrease in vehicle value over time due to wear and aging. This is important to consider because depreciation affects both TCO and ROI. | Tires: In-time purchasing and replacing tires that wear out can ensure safety and operational efficiency. |
Taxes and fees are the following: Vehicle registration expenses, taxes, and other government fees associated with fleet ownership.
Calculating Cost-Per-Mile
Cost-per-mile (CPM) is an essential indicator of vehicle efficiency. It allows you to assess how economically profitable vehicles are used in the fleet. The CPM calculation process involves several key steps:
- First, it is necessary to take into account all the expenditures associated with operating the vehicle. This includes fuel, maintenance, repair, insurance, depreciation, and other expenses. All these items are collected for a certain period, for example, a month or a year.
- Secondly, you have to determine the total cost of operating the vehicle for this period.
- Thirdly, you should calculate the total number of miles (or kilometers) traveled by a vehicle during the same period. This information can be obtained using a vehicle odometer or GPS monitoring system.
- Finally, TCO is divided by the total number of miles traveled to get the cost per mile. This indicator helps assess each vehicle's performance and understand which vehicles are most cost-effective to use.
Types of Costs in Fleet Management
Fleet management requires taking into account different types of expenditures that affect the overall business profitability. Each this type has its own characteristics and requires an appropriate approach to be minimized.
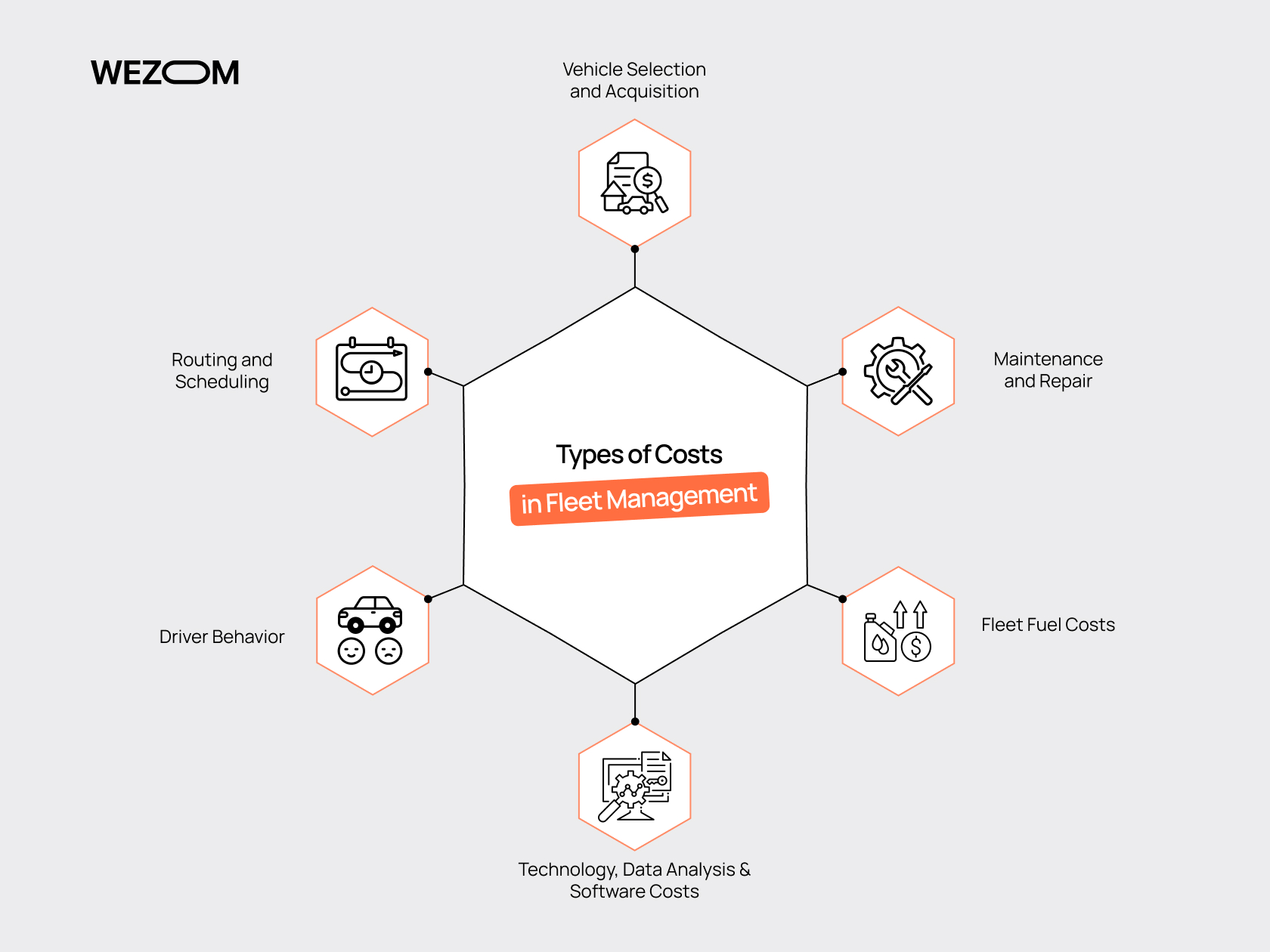
Vehicle Selection and Acquisition
Choosing and purchasing suitable vehicles involves the analysis of various factors such as their initial cost, operating costs, fuel economy, and reliability. The right choice also depends on maintenance and repair. In addition, it is vital to consider the specifics of the transportation that the fleet will perform to choose the proper vehicles for specific tasks.
For example, it is reasonable to select economical trucks with an extensive range for long trips and maneuverable and compact cars – for urban transportation.
Maintenance and Repair
Regular vehicle maintenance and repair are vital to preventing severe breakdowns and extending the fleet's life. Regular checks and maintenance allow you to identify problems in the early stages and eliminate them before they become too expensive. In addition, it ensures the continuous operation of vehicles. Therefore, in-time maintenance pays off over time as it lowers the risk of unexpected downtime.
Routing and Scheduling
Using specialized programs for routing helps to find the shortest and fastest routes. For example, the introduction of automated planning systems will allow you to optimize the distribution of tasks among vehicles, considering their current load and location. Also, with correct route planning, you will be able to avoid traffic jams, eliminate waiting times, increase the number of completed orders, and, in general, improve customer service.
Technology, Data Analysis & Software Costs
Investments in technology and software, such as transport management systems (TMS), can help you automate many processes. Specifically, modern technologies can control all management aspects, from vehicle monitoring to cost analysis, at the same time, eliminating human factor and responding the changes in time. Such a software can also provide you with real-time data analytics for making informed decisions and optimizing expeses at all stages of fleet management.

Fleet Fuel Costs
Fuel is one of the most oversized expenditure in fleet management. To save your budget, you can introduce modern navigation technologies and fuel consumption monitoring systems that allow you to optimize routes and reduce unnecessary runs. In addition, you can train your drivers to avoid sudden accelerations and braking. Also, consider the use of alternative fuels such as electricity or natural gas.
Driver Behavior
Inefficient driving methods, such as speeding, sudden braking, or unnecessary engine idling, can affect the fuel costs and vehicle wear. Instead, using driver behavior monitoring systems helps to identify and fix such problems. Conducting regular training and regular checking feedback based on tracking data can increase your business performance and, at the same time, reduce overheads.
Case Study of TMS with Cost Analysis Module
Let’s check a specific case from our portfolio, Gamma TMS. For this project, we developed a special cost analysis module that allows our client to significantly optimize the fleet management processes.
This module automatically collects and processes data on all expenses associated with vehicle operation, providing accurate and timely real-time information thanks to integration with GPS trackers and other monitoring systems.
This module also includes powerful forecasting functions, allowing managers to see exactly where funds are spent and how they can be optimized. In addition, the module has advanced features on route optimization and task distribution, avoiding unnecessary runs.
In general, by implementing this module, our client minimized operating costs and improved fleet management efficiency. Here, you can learn more about the Gamma TMS case:
Tips to Reduce Fleet Management Costs
As you can understand, reducing fleet management costs is critical to improving business profitability. So, here are some detailed tips to help achieve this goal.
- Choose economical vehicles.
Choosing suitable cars not only reduces fuel expenditures but also minimizes CO2 emissions. For instance, modern cars have improved engines with high fuel efficiency. You can also consider hybrid and electric vehicles, which have even lower operating costs.
- Maintain and repair vehicles regularly.
Regular maintenance includes oil changes, brake system checks, fluid level control, and other preventive measures. These actions help keep vehicles in good condition, eliminating unexpected breakdowns and extending the life of vehicles.
- Use smart routing.
Specialized programs for route planning help find the shortest and fastest routes. In addition, efficient routing helps slow down vehicle wear. This boosts drivers’ productivity and overall transportation efficiency.
- Invest in driver training.
Drivers who know how to save fuel, avoid sudden accelerations and braking, follow traffic rules, and kno how to minimize vehicle wear can significantly improve your budget management. Actually, that’s why you should consider their regular training and implementing motivational programs for drivers.
- Apply modern technology and software.
Modern technologies and software, such as transport management systems (TMS), allow you to automate many processes and improve the accuracy of cost management. These systems provide accurate monitoring of fuel and fleet maintenance costs, helping identify trends and anomalies in expenses and, thus, enabling you to respond to changes in time and make informed decisions.
- Choose an experienced TMS developer.
Choosing an experienced TMS developer is key to successfully automating fleet management processes. Our experience in developing and implementing TMS helps businesses boost their financial visibility over all directions. We offer advice and support to help you choose and implement the best solutions for your business. Contact us to learn more about how our fleet management cost analysis

