Today, the use of agricultural technology allows businesses to increase yields and improve process control. For example, when farmers use methods such as field performance monitoring, they can greatly boost their income and eliminate downtime. Today we will take a closer look at the use of technology in agriculture.
What Is Agriculture Technology?
Agricultural technology, or agritech, unifies methods that improve the productivity of all agricultural processes. These methods may be implemented in transport, robotics, drones, mobile devices, computers, satellites, and software.
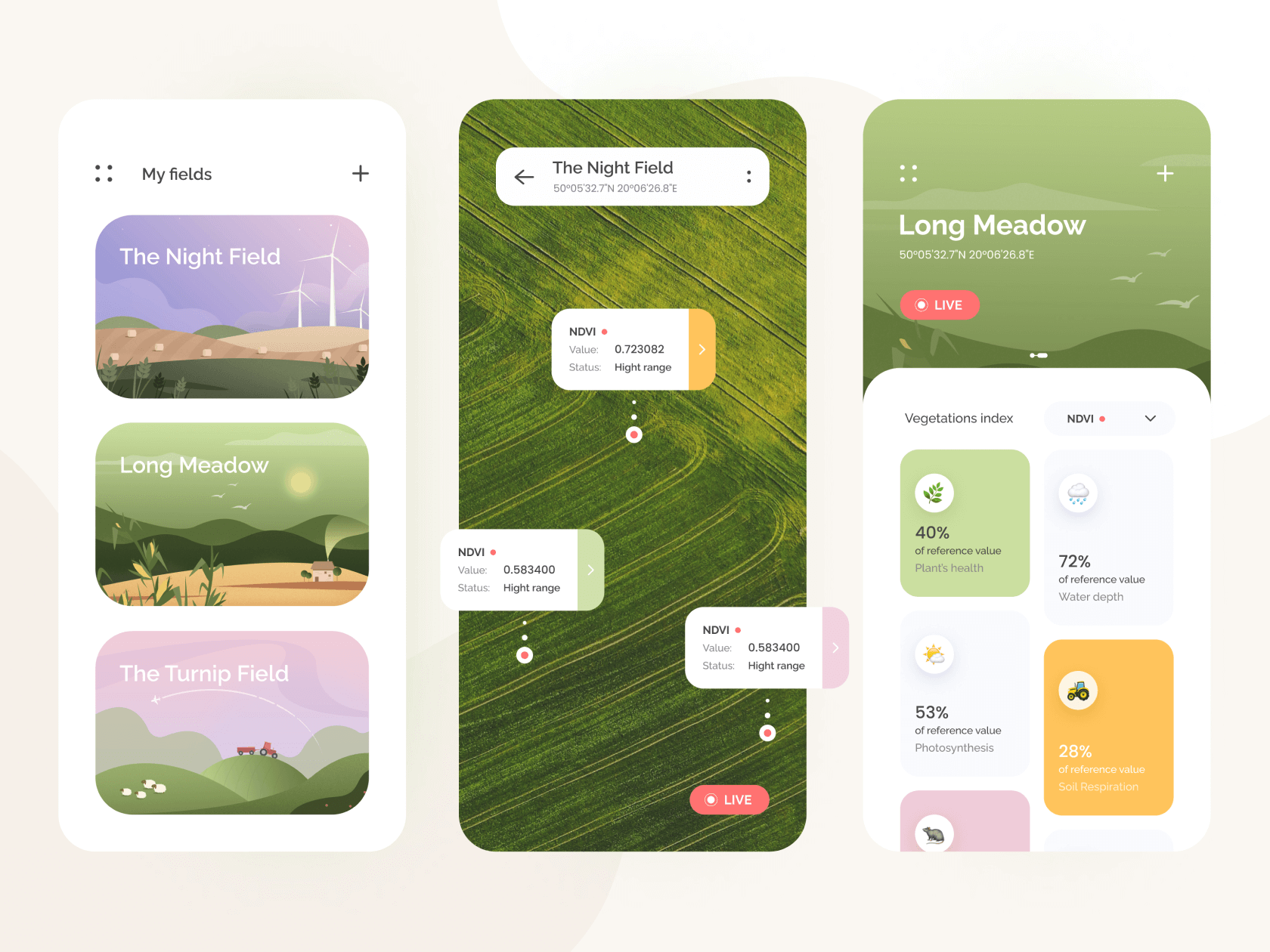
Importance Of Technology In Agriculture
Agrotech helps to increase the efficiency and convenience of working processes within the agriculture business. Therefore, agricultural enterprises started to move away from the use of resources "by eye" and use new farming technology that allowed them to accurately determine the amount and place where fertilizers, water, and other resources should be delivered.
Benefits Of Technology In Agriculture
The use of agrotech brings undoubted benefits to all participants in the agri-food chain. Here are some of them:
- lower overhead costs due to reducing the use of resources;
- minimized impact of chemicals on the environment;
- increased productivity with less labor;
- simpler communication and coordination between farmers, agronomists, and other workers due to the use of mobile devices;
- easier access to agricultural insurance and financial services;
- elimination of risks caused by damage associated with natural disasters and pests;
- better product quality;
- comprehensive monitoring of nutrient deficiencies in plants;
- easier building of production models that anticipate problems on the farm;
- accurate yield estimation for future growing seasons.
Evolution Of Agriculture Technology
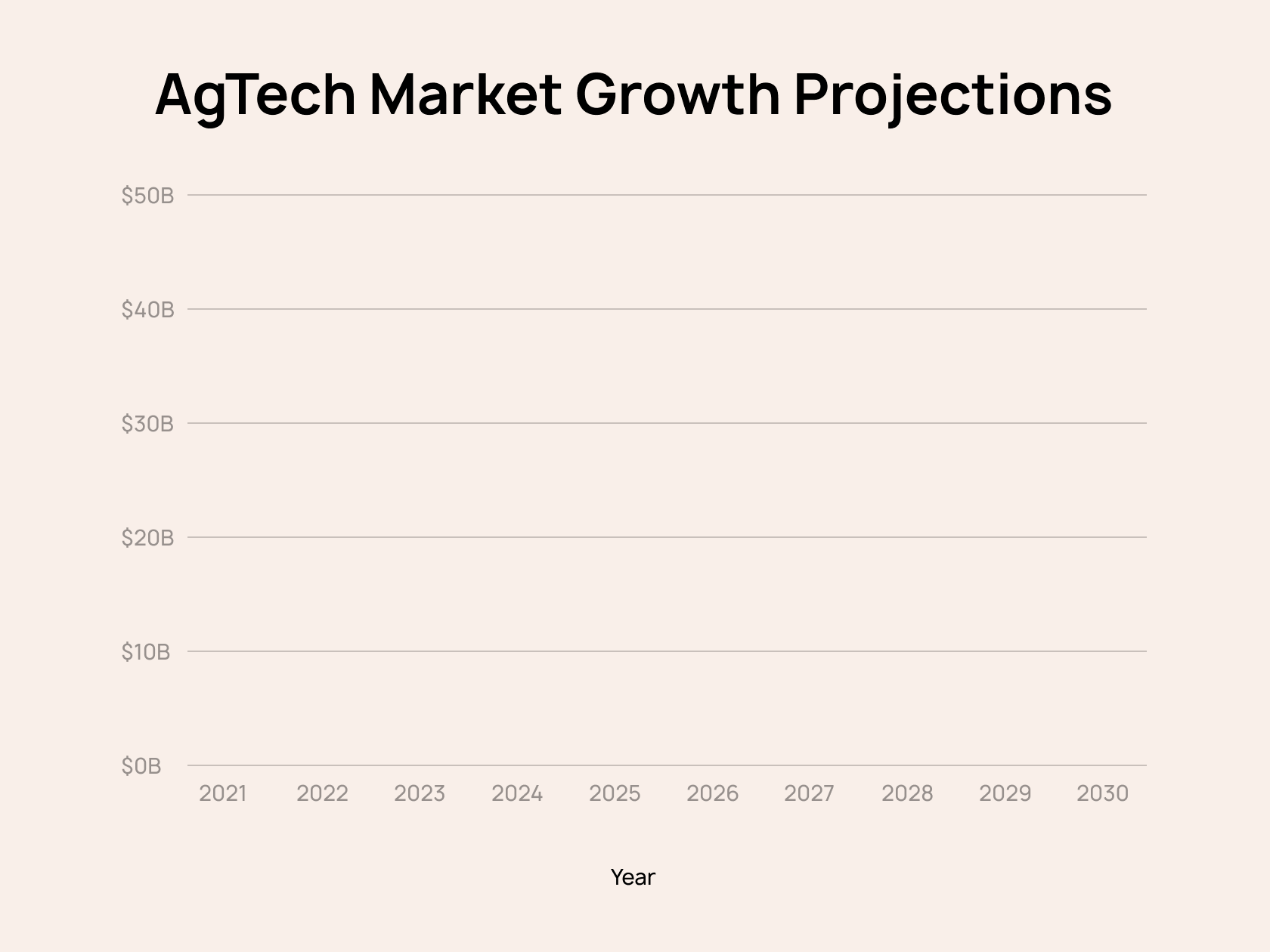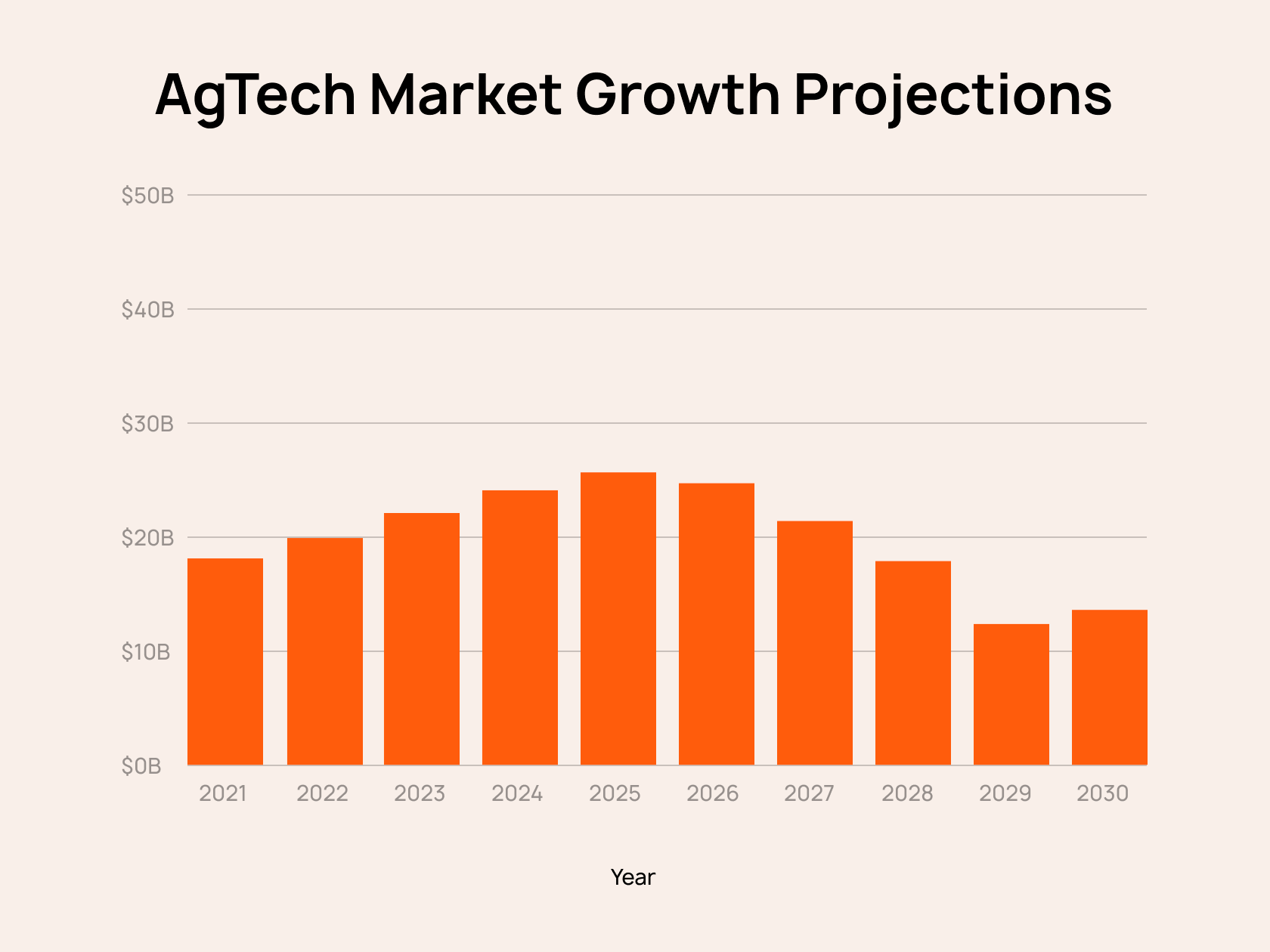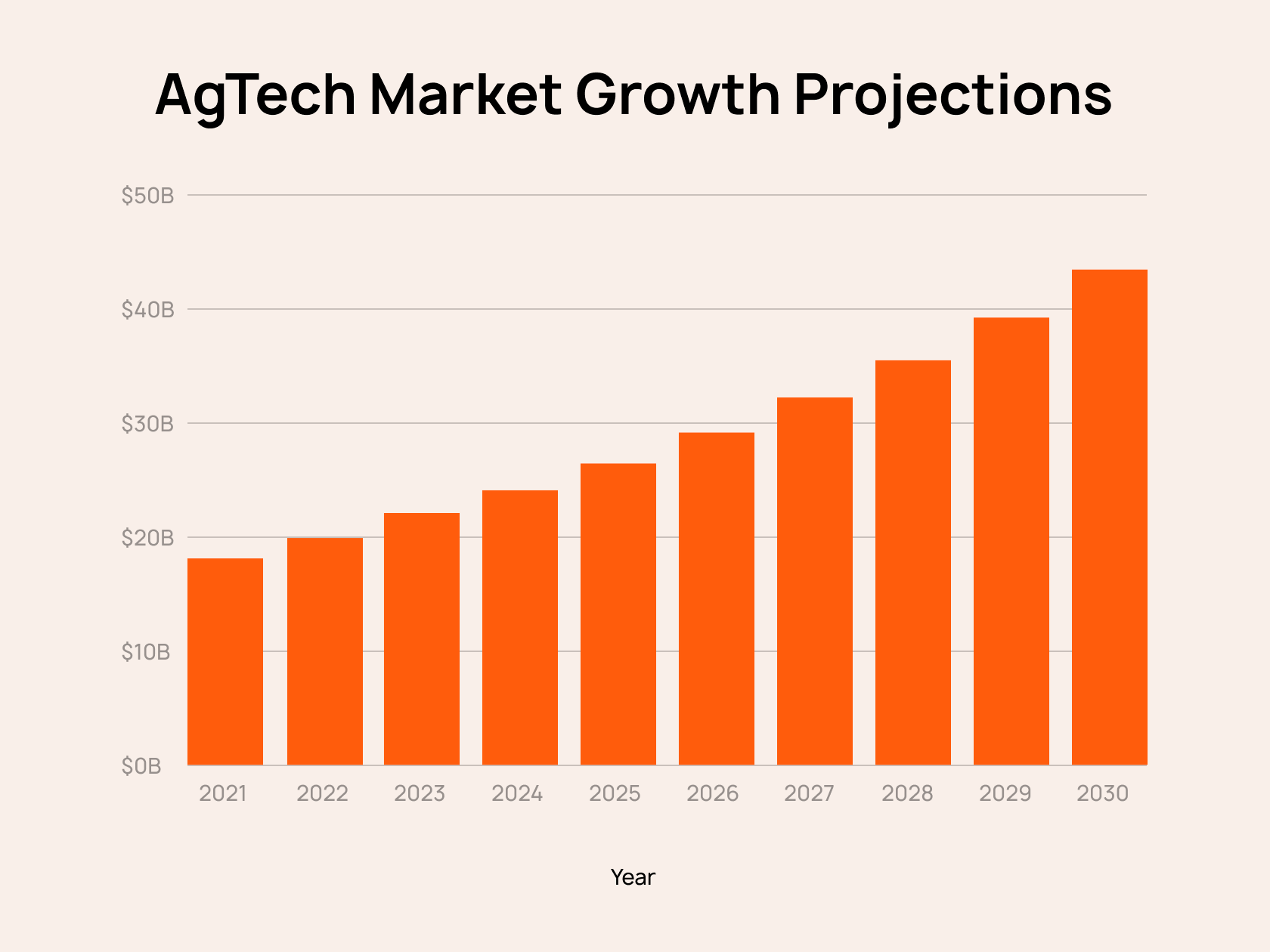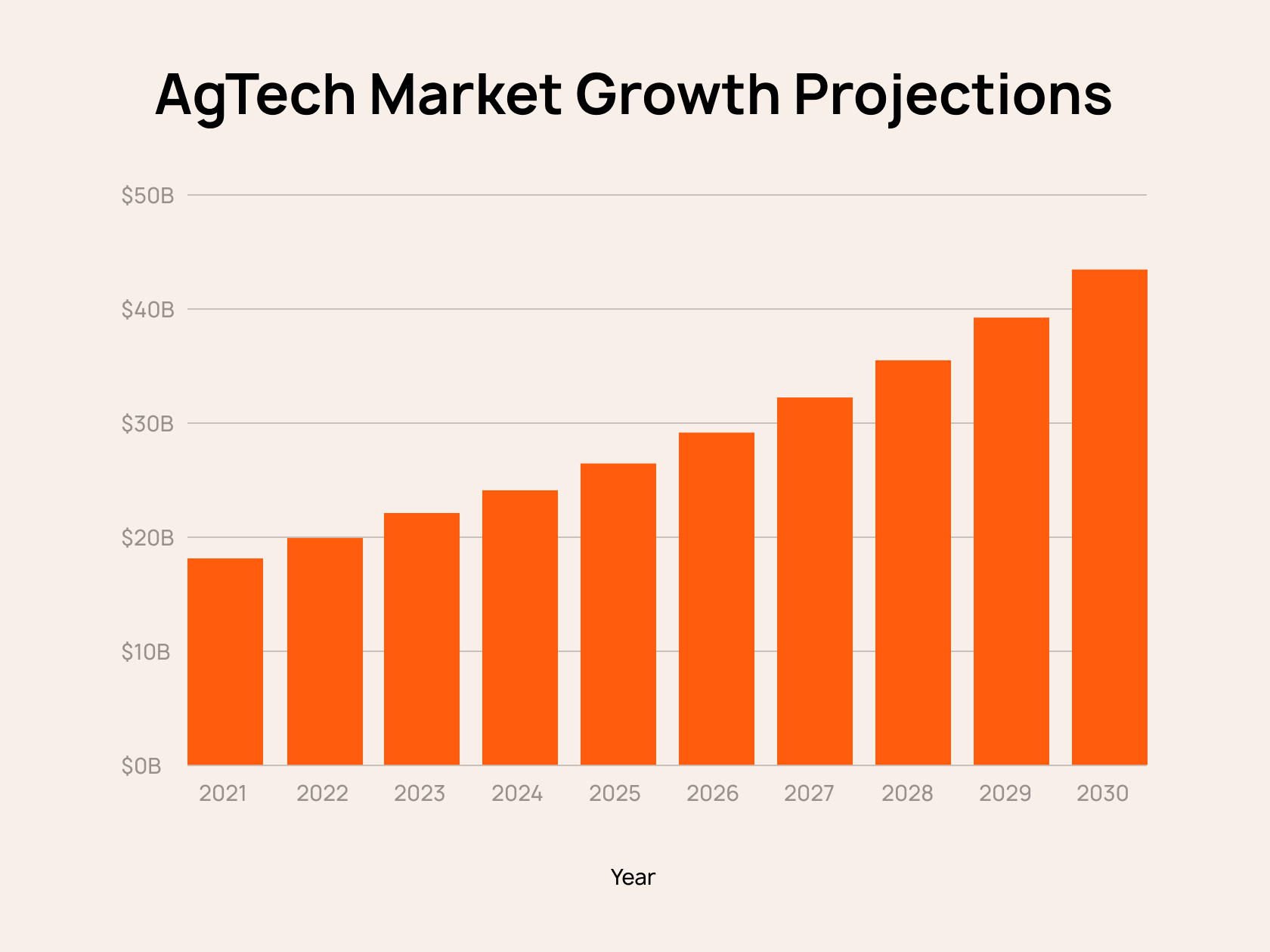
The global agritech market is on the rise — it is expected to surpass $40 billion by 2030. Indeed, until the beginning of the 20th century, the technological model of agricultural production was low-productive. For instance, the so-called Agriculture 1.0 era is famous for the invention of the plow and the use of draft animals. At the same time, Agriculture 2.0 is well-known for the advent of tractors. From that moment, agrotech began to develop due to a sharp increase in technological progress.
Agriculture 3.0, Or Precision Farming
Agriculture 3.0 is still agriculture – people continued to use the soil and were highly dependent on natural and climatic conditions. But the way of organizing production, technique, and technology allowed them to intensify and optimize all processes and procedures significantly.
Agriculture 4.0, Or Connected Farming
Agriculture 4.0 lies in all available means of mechanization and automation of production, supplemented by IoT. This can be new software and hardware, including robots, ranging from systems with limited mobility, such as robotic milking parlors, feeders, and manure cleaners, to the ones that perform specific field tasks such as planting seeds, weeding or spraying, automated pasture grazing systems, and UAVs.
Agriculture 5.0, Or Digital Farming
As for Agriculture 5.0, this concept already implies a complete digitization of agricultural processes based on next-generation methods and tools. A particular example of such solutions is those based on 5G, one of the most advanced technologies for wireless connection over long distances. In addition to the use of such breakthrough technologies, this generation of agritech is also characterized by increased data collection efficiency, their accuracy, and high performance in all processes where this data takes part.
Advancements And Innovations In Agriculture Technology
Even for short periods of time, such as a year or two, it is impossible not to notice innovations that bring significant improvements to the field of agriculture. Agritech makes seeds more resilient, waste recycling more efficient, and work processes as automated as possible.
Negative Impacts Of Agricultural Technology: Are There Any?
We can see the most negative consequences of the introduction of advanced technologies in the agricultural industry in the ecosystem:
- potential contamination of soil and water due to the use of pesticides;
- decrease in biodiversity due to the disappearance of natural species of flora and fauna;
- greenhouse effect provoked by the use of technology.
What Types Of Precision Agricultural Technology Are Now In Use?
Let's now look at particular cases of innovations in agriculture.

GPS
With the help of GPS data, all processes associated with the need to determine and plan locations for specific tasks can be optimized. Thanks to this, companies in this field can reduce the cost of fuel, electricity, and other resources necessary to achieve their goals. Also, GPS can be used for “traditional” logistics purposes to improve supply chains and shorten the delivery paths for the transportation of necessary cargo.
Robotic process automation
Robotization of complex physical processes that are regularly repeated can reduce the burden on human resources, increase the volume of work (since, unlike a human, a robot can work around the clock), reduce the risks associated with the human factor, and also protect workers from the harmful effects of pesticide fumes and other substances hazardous to health.
Big data
Big data allows companies to make smarter data-driven decisions and get a clearer picture of what's going on in their farmlands. Moreover, obtaining the necessary analytics can now take only a few minutes instead of hours, days, and even weeks, as was the case with manual work.
Internet of Things
Big data technologies work especially well when combined with the Internet of Things technologies, allowing companies to analyze “raw” data in real time. In particular, smart sensors can be used for chemical analysis of soil composition, measurement of air humidity, accumulation of weeds and pests, etc.
Geographic informational systems
Geographic information systems (GIS) consisting of satellites and drones can be used to effectively visualize spatial data to be applied to local needs. In particular, these devices allow, without direct human participation, to explore specific locations and obtain data from them that will be useful for performing specific agricultural work – sowing, tillage, harvesting, eliminating pests, etc.
How Does Technology Impact Agriculture?
Currently, the main task of agriculture technology vendors who work to expand the capabilities of agritech is to eliminate or reduce the possible negative consequences caused by the introduction of specific agritech technologies.
In particular, we are talking about the potential reduction in the volume of pesticides used, the elimination of the need for deforestation and the use of resource-intensive agricultural machinery, as well as the optimization of the location of agricultural land, taking into account the natural flora and fauna that can be destroyed.
Conclusion
It is impossible not to notice how the introduction of technology has changed the agricultural industry over the years. Overhead costs are reduced, advanced farming technologies cover more and more processes that were previously performed by humans, and new approaches to achieving the highest yields emerge. Therefore, this industry will develop for many years to come since each time certain goals are achieved, there will always be risks and potentially negative consequences that will also need to be dealt with.